Best Treatment for Actinic Keratosis on Face
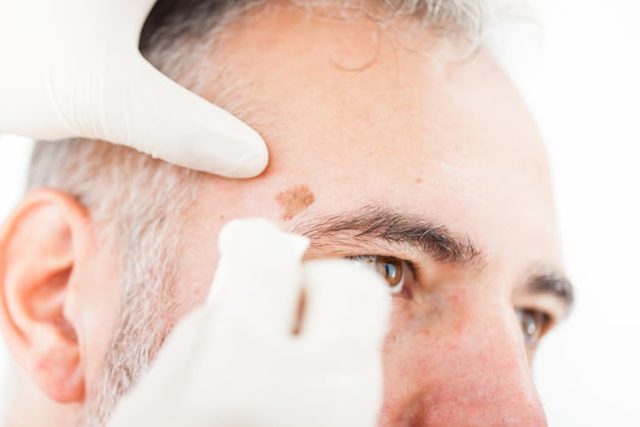
Actinic keratosis (AK) is a common skin condition caused by prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, leading to rough, scaly patches on the skin, especially on the face, scalp, and hands. Since these lesions have the potential to develop into skin cancer, it’s important to treat them early. The best treatment options for actinic keratosis on the face, focusing on both medical and natural remedies.
Actinic Keratosis
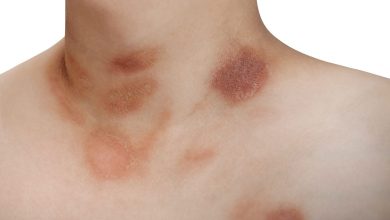
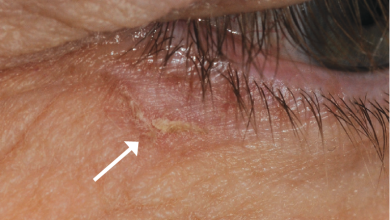
Actinic keratosis is characterized by rough, dry, or scaly patches of skin that are often pink, red, or brown. These patches can be itchy or tender and usually appear on areas frequently exposed to the sun, such as the face, ears, neck, and scalp. People with fair skin, a history of sunburns, or a weakened immune system are more likely to develop AK.
Best Medical Treatments for Actinic Keratosis on the Face
- Cryotherapy
Cryotherapy is one of the most common treatments for actinic keratosis. It involves freezing the affected skin with liquid nitrogen, which causes the abnormal cells to die and slough off. This method is quick, relatively painless, and effective for treating individual lesions.
- Topical Medications
- 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU): This chemotherapy cream works by destroying the abnormal skin cells. It is applied directly to the lesions for several weeks, causing the treated area to become red and sore before healing.
- Imiquimod Cream: Imiquimod stimulates the immune system to produce interferon, a chemical that attacks cancerous and precancerous cells. This cream is applied several times a week for a few weeks, and it may cause inflammation, redness, and peeling.
- Diclofenac Gel: Diclofenac is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that reduces inflammation and promotes the death of abnormal cells. It is less irritating than 5-FU or imiquimod, making it suitable for patients with sensitive skin.
- Ingenol Mebutate Gel: This is a plant-derived treatment that causes cell death and an immune response to eliminate abnormal cells. It is applied for just a few days, and the skin usually heals within a few weeks.
- Photodynamic Therapy (PDT)
Photodynamic therapy is a highly effective treatment that combines a photosensitizing agent with light exposure to destroy abnormal cells. The photosensitizing agent is applied to the lesions, and after it is absorbed, the area is exposed to a specific wavelength of light. This activates the drug, causing it to produce a reaction that destroys the damaged cells.
- Laser Therapy
Laser therapy uses concentrated beams of light to target and destroy abnormal skin cells. This method is precise and minimizes damage to surrounding tissue. It is often used for thicker or more persistent lesions.
- Chemical Peels
Chemical peels involve applying a chemical solution to the skin, causing the top layer to peel off. This process removes the damaged outer layer of skin, promoting the growth of new, healthy skin. Trichloroacetic acid (TCA) peels are commonly used for treating actinic keratosis.
Natural Remedies and Preventative Measures
While medical treatments are the most effective for actinic keratosis, some natural remedies and lifestyle changes can help manage the condition and prevent further damage:
- Aloe Vera
Aloe vera has anti-inflammatory and healing properties that can soothe irritated skin. Applying aloe vera gel to the affected area may help reduce redness and promote healing.
- Green Tea Extract
Green tea contains polyphenols, which have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Applying green tea extract topically can help protect the skin from UV damage and may reduce the risk of developing new lesions.
- Diet and Supplements
A diet rich in antioxidants, such as vitamins C and E, can help protect the skin from damage caused by free radicals. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish oil, may also reduce inflammation and support skin health.
- Sun Protection
Preventing further sun damage is crucial for managing actinic keratosis. Always use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher, wear protective clothing, and avoid sun exposure during peak hours.
Conclusion
The best treatment for actinic keratosis on the face depends on the number, size, and location of the lesions, as well as the patient’s skin type and overall health. Medical treatments such as cryotherapy, topical medications, photodynamic therapy, laser therapy, and chemical peels offer effective solutions for eliminating actinic keratosis lesions. Natural remedies and preventive measures can complement these treatments and help maintain healthy skin. Consulting a dermatologist is essential to determine the most appropriate treatment plan tailored to individual needs, ensuring the best possible outcomes in managing actinic keratosis.