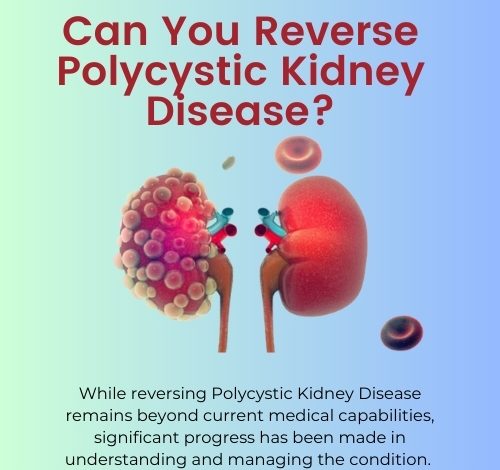
Can You Reverse Polycystic Kidney Disease?
Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD) is a genetic disorder characterized by the growth of numerous cysts in the kidneys, leading to a gradual decline in kidney function. For those affected, PKD presents a significant challenge, not only physically but also emotionally. This raises a critical question: Can PKD be reversed? While the journey to a definitive cure continues, medical advancements and lifestyle strategies offer hope and tools for effective management. Whether PKD can be reversed and discuss the latest scientific breakthroughs, lifestyle modifications, and holistic approaches to address the disease.
Understanding Polycystic Kidney Disease
Definition and Types
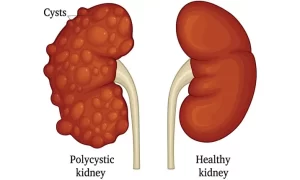
Polycystic Kidney Disease is a chronic condition in which clusters of cysts develop primarily in the kidneys, leading to organ enlargement and loss of function over time. There are two main types of Polycystic Kidney Disease:
- Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease (ADPKD): The most common form, affecting adults, with symptoms typically appearing between ages 30 and 50.
- Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease (ARPKD): A rarer and more severe form, usually diagnosed in infancy or early childhood.
Symptoms and Complications
PKD symptoms vary but often include:
- High blood pressure.
- Pain in the abdomen or sides.
- Blood in the urine (hematuria).
- Frequent urinary tract infections (UTIs).
- Kidney stones.
Over time, complications such as kidney failure, liver cysts, and cardiovascular problems can arise, significantly impacting quality of life.
Causes and Genetic Factors
Polycystic Kidney Disease is primarily caused by mutations in specific genes (“PKD1” and “PKD2” for ADPKD, and “PKHD1” for ARPKD). These mutations disrupt normal cellular function, leading to cyst formation. While the condition is hereditary, spontaneous mutations can also occur in families without a history of Polycystic Kidney Disease.
Impact on Kidney Function
As cysts grow, they replace healthy kidney tissue, reducing the kidney’s ability to filter waste and balance fluids. Without intervention, this can lead to end-stage kidney disease (ESKD), requiring dialysis or a kidney transplant.
Can PKD Be Reversed?
Current Understanding
At present, Polycystic Kidney Disease is considered irreversible, as the damage caused by cyst formation is permanent. However, advances in medical science are shifting the focus toward early diagnosis, disease management, and the potential for future breakthroughs.
Managing vs. Reversing
The primary goal of current Polycystic Kidney Disease treatments is to slow disease progression and manage symptoms. While this does not equate to reversal, it can significantly delay complications and improve quality of life.
The Role of Early Diagnosis
Identifying Polycystic Kidney Disease early allows for timely intervention, which can slow cyst growth, preserve kidney function, and reduce the risk of severe complications. Routine screenings for at-risk individuals are essential.
Advances in Medical Research
Gene Therapies Under Development
Gene editing technologies, such as CRISPR, hold promise for addressing the root cause of Polycystic Kidney Disease by correcting genetic mutations. While still in experimental stages, these therapies could potentially halt or reverse cyst formation in the future.
Promising Drugs
- Tolvaptan: This FDA-approved medication slows cyst growth in ADPKD by inhibiting the hormone vasopressin. Studies show it can delay disease progression, although it does not reverse existing damage.
- Other drugs under investigation include mTOR inhibitors and somatostatin analogs, which aim to reduce cyst size and inflammation.
Regenerative Medicine and Stem Cell Research
Regenerative medicine explores the potential of stem cells to repair or replace damaged kidney tissue. While still in its infancy, this field offers hope for future therapies that could restore kidney function.
Potential Breakthroughs
Recent studies have identified pathways involved in cyst formation, opening doors to targeted therapies. For example, research into polycystin proteins (produced by PKD1 and PKD2 genes) may lead to novel treatments.
Lifestyle Modifications to Manage PKD
Diet and Nutrition
A kidney-friendly diet can play a crucial role in managing Polycystic Kidney Disease. Key recommendations include:
- Reducing sodium intake to control blood pressure.
- Opting for lean proteins and plant-based diets to reduce kidney strain.
- Staying hydrated but avoiding excessive fluid intake to prevent overburdening the kidneys.
Hydration and Avoiding Nephrotoxins
Proper hydration supports kidney health, but it’s essential to avoid substances that can harm the kidneys, such as excessive caffeine, alcohol, and over-the-counter painkillers like ibuprofen.
Stress Management
Chronic stress can worsen Polycystic Kidney Disease symptoms by increasing blood pressure. Techniques such as mindfulness meditation, yoga, and deep breathing exercises can help manage stress effectively.
Exercise Recommendations
Regular physical activity helps maintain a healthy weight, reduce blood pressure, and improve overall well-being. Low-impact exercises like walking, swimming, and cycling are ideal for PKD patients.
Natural and Holistic Approaches
Herbal Remedies
Some Natural Remedies for Polycystic Kidney Disease, such as nettle leaf and cranberry extract, may support kidney health by reducing inflammation and preventing infections. However, these should be used under medical supervision.
Traditional Medicine Practices
Ayurvedic and Traditional Chinese Medicine approaches often emphasize balancing the body’s energy and detoxifying the kidneys. While not scientifically proven, these practices may offer complementary support.
The Role of Supplements
Certain supplements, such as omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin D, and antioxidants, may help reduce inflammation and oxidative stress, potentially slowing disease progression.
Emotional and Mental Health Support
Coping with a Chronic Illness
Living with PKD can be emotionally challenging. Patients often experience feelings of anxiety, fear, or depression. Acknowledging these emotions and seeking support is essential.
Building a Supportive Community
Joining PKD-focused support groups, either online or in person, can provide valuable connections, shared experiences, and emotional encouragement.
The Role of Counseling and Therapy
Professional counseling can help patients navigate the emotional aspects of chronic illness and develop resilience and coping strategies.
Real-Life Stories of PKD Patients
Inspirational Accounts
Many Polycystic Kidney Disease patients have successfully managed their condition through a combination of medical treatments, lifestyle changes, and sheer determination. Their stories highlight the importance of staying proactive and hopeful.
Lessons Learned
From prioritizing self-care to advocating for research, these individuals emphasize the importance of being informed and involved in one’s healthcare journey.
The Role of Technology in PKD Care
Telemedicine
Virtual consultations enable regular monitoring and easy access to specialists, particularly for those in remote areas.
Innovative Apps and Tools
Apps designed for kidney disease management can help track symptoms, medication schedules, and dietary choices, empowering patients to stay on top of their health.
Conclusion
While reversing Polycystic Kidney Disease remains beyond current medical capabilities, significant progress has been made in understanding and managing the condition. Advances in research, combined with lifestyle modifications and holistic approaches, offer hope for improved quality of life and slowed disease progression. As science continues to evolve, the dream of reversing Polycystic Kidney Disease may one day become a reality. For now, staying informed, proactive, and engaged with healthcare providers is the best path forward for those living with Polycystic Kidney Disease. Remember, every step taken today contributes to a brighter future for Polycystic Kidney Disease patients worldwide.